Phalloidin
from Amanita phalloides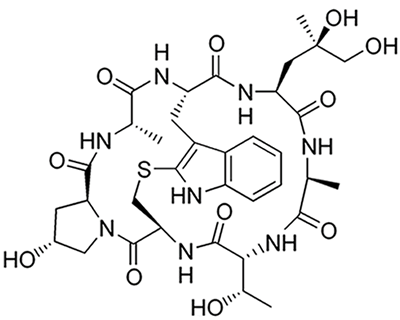
 ...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Applications
Inhibition of actin depolymerization;
Stabilization of actin filaments.
Description
Phalloidin binds to actin filaments and inhibits their depolymerization by specific interaction at the interface of adjacent monomers of the filaments. Phalloidin is a bicyclic heptapeptide with high affinity for actin filaments and lower affinity for actin monomers. Binding of Phalloidin leads to a decrease in the rate constant for the dissociation of actin monmers from filament ends. This results in a stabilization of filaments, used in many assays where stable actin filaments are demanded.
Phalloidin is also inhibits the ATP-ase activity of F-actin. Binding arrests actin monomers in a specific G-actin state and stabilizes filament structure by strongly reducing the rate constant for monomer dissociation, an event associated with the trapping of ADP.
Phalloidin binds in 1:1 molar ratio to G-actin, strongly promotes actin polymerization, and stabilizes actin filaments.
Units
100µM in 500µl (dry component, reconstitute upon arrival)
► 500µl of a 100µM solution stabilize 2mg actin at a 1:1 molar ratio.
 Product DataSheet
Product DataSheet
 Material and Safety Data Sheet
Material and Safety Data Sheet